potential energy
Potential EnergyAn object can store energy as the result of its position. For example, the heavy heavy ball of a demolition machine is storing energy when it is held at an elevated position. This stored energy of position is referred to as potential energy. Similarly, a drawn bow is able to store energy as the result of its position. When assuming its usual position (when not drawn), there is no energy stored in the bow. Yet when its position is altered from its usual equilibrium position, the bow is able to store energy by virtue of its position. This stored energy of position is referred to as potential energy. Potential energy is the stored energy of position possessed by an object.

Gravitational Potential Energy

Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object as the result of its vertical position or height. The energy is stored as the result of the gravitational attraction of the Earth for the object. The gravitational potential energy of the massive ball of a demolition machine is dependent on two variables - the mass of the ball and the height to which it is raised. There is a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the mass of an object. More massive objects have greater gravitational potential energy. There is also a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the height of an object. The higher that an object is elevated, the greater the gravitational potential energy. These relationships are expressed by the following equation:
PEgrav = m * g * h
m represents the mass of the object, h represents the height of the object and g represents the acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s/s on Earth).
Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in elastic materials as the result of their stretching or compressing. Elastic potential energy can be stored in rubber bands, bungee chords, trampolines, springs, an arrow drawn into a bow, etc. The amount of elastic potential energy stored in such a device is related to the amount of stretch of the device - the more stretch, the more stored energy.
Springs are a special instance of a device which can store elastic potential energy due to either compression or stretching. A force is required to compress a spring; the more compression there is, the more force which is required to compress it further. For certain springs, the amount of force is directly proportional to the amount of stretch or compression (x); the constant of proportionality is known as the spring constant (k).

If a spring is not stretched or compressed, then there is no elastic potential energy stored in it. The spring is said to be at its equilibrium position. The equilibrium position is the position that the spring naturally assumes when there is no force applied to it. In terms of potential energy, the equilibrium position could be called the zero-potential energy position. There is a special equation for springs which relates the amount of elastic potential energy to the amount of stretch (or compression) and the spring constant. The equation is

Summary:
potential energy is the energy which is stored in an object due to its position relative to some zero position. An object possesses gravitational potential energy if it is positioned at a height above (or below) the zero height. An object possesses elastic potential energy if it is at a position on an elastic medium other than the equilibrium position.
resistors

Bad Beers Rip Our Young Guts But Vinta Gives Well.
A resistor is a two-terminal electrical or electronic component that resists an electric current by producing a voltage drop between its terminals in accordance with Ohm's law: R= V/I .The electrical resistance is equal to the voltage drop across the resistor divided by the current through the resistor. Resistors are used as part of electrical networks and electronic circuits.
Working with very imprecise measurements, Ohm was able to determine that voltage and current for any fixed geometrical structure built from conducting material satisfied a relationship:
V = I R
where:
V is the voltage across the device,
I is the current flowing through the device,
R is a constant.
R depends upon the material from which the device is constructed and the geometry of the material.
lured into a deep sleep at Monday, October 15, 2007 0 person(s) commented while I sleep
radiation
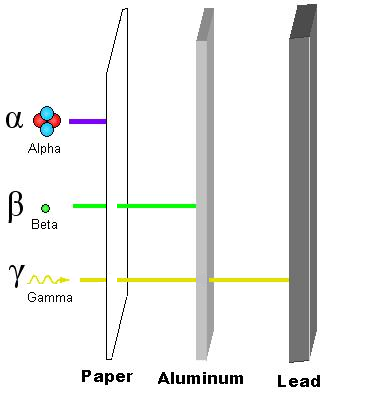
Particle Radiation
Radiation as used in physics, is energy in the form of waves or moving subatomic particles. Radiation can be classified as ionizing or non-ionizing radiation, depending on its effect on atomic matter. The most common use of the word "radiation" refers to ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation has enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules while non-ionizing radiation does not. Radioactive material is a physical material that emits ionizing radiation.
Types of Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation: (Energy in the form of electromagnetic waves or photons.)
Non-ionizing
Thermal radiation (heat radiation)
Radio waves
Microwave radiation, as used in microwave ovens
Infrared radiation (IR), produced by heat
Visible light - light that is visible to the naked eye
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than soft X-rays.
Ionizing
X-rays, used in radiography for medical diagnosis
Gamma radiation, usually emitted by radioactive atoms
Particle radiation: (Energy in the form of moving subatomic particles.)
Alpha radiation, composed of the nuclei of helium-4 atoms
Beta radiation, consisting of energetic electrons or positrons
Neutron radiation, consisting of neutrons
The effect of magnetic and electric fields on these particles/rays:
Positively charged alpha particles are deflected by both magnetic and electric fields.
Negatively charged beta particles are also deflected by both types of fields, but in the opposite direction from alpha particles.
Neutrons and electromagnetic radiation have no charge, and are unaffected by electromagnetic fields.
lured into a deep sleep at Monday, October 15, 2007 0 person(s) commented while I sleep
